Dell in stock market what is beta definition
Important Announcement FlipHTML5 Scheduled Server Maintenance on GMT Sunday, June 26th, 2: FlipHTML5 site will be inoperative during the times indicated! You own three stocks: What are the portfolio weights of the three stocks in your portfolio?
What is the expected return of your portfolio? What are the new portfolio weights? Apple 12 0. Consider a world that only consists of the three stocks shown in the following table: Calculate the total value of all shares outstanding currently.
What fraction of the total value outstanding does each stock make up? Stock Total Number of Current Price Expected Value b. There are two ways to calculate the expected return of a portfolio: Which return is higher? Both calculations of expected return of a portfolio give the same answer. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Using the data in the following table, estimate a the average return and volatility for each stock, b the covariance between the stocks, and c the correlation between these two stocks.
What is the return each year of this portfolio? Based on your results from part a, compute the average return and volatility of the portfolio.
Show that i the average return of the portfolio is equal to the average of the average returns of the two stocks, and ii the volatility of the portfolio equals the same result as from the calculation in Eq. Explain why the portfolio has a lower volatility than the average volatility of the two stocks.
The portfolio has a lower volatility than the average volatility of the two stocks because some of the idiosyncratic risk of the stocks in the portfolio is diversified away.
Using the data from Table Suppose two stocks have a correlation of 1. If the first stock has an above average return this year, what is the probability that the second stock will have an above average return? Because the correlation is perfect, they move together always and so the probability is 1. In which cases is the volatility lower than that of the original stocks? What portfolio of these two stocks has zero risk? If Tex and Mex are uncorrelated, a.
What portfolio of the two stocks has the same volatility as Mex alone? What portfolio of the two stocks has the smallest possible volatility?
Estimate the volatility of an equally weighted portfolio with a 1 stock, b 30 stocks, c stocks. What is the volatility of the portfolio as the number of stocks becomes arbitrarily large? What is the average correlation of each stock with this large portfolio? You currently hold both stocks. Which will increase the volatility of your portfolio: So, volatility increases if we sell A and add B. You currently hold a portfolio of three stocks, Delta, Gamma, and Omega. What is the highest possible volatility of your portfolio?
If your portfolio has the volatility in a , what can you conclude about the correlation between Delta and Omega? If the two stocks are uncorrelated, a. What is the expected return and volatility of an equally weighted portfolio of the two stocks?
Given your answer to a , is investing all of your money in Molson Coors stock an efficient portfolio of these two stocks? Is investing all of your money in Ford Motor an efficient portfolio of these two stocks? No, dominated by portfolio. If these two stocks were perfectly negatively correlated i.
Calculate the portfolio weights that remove all risk. If there are no arbitrage opportunities, what is the risk-free rate of interest in this economy? If the two stocks are perfectly correlated negatively, they fluctuate due to the same risks, but in opposite directions.
We can check this using Eq. Because this portfolio has no risk, the risk-free interest rate must also be We can use Eq. Would the expected return of the portfolio rise or fall? Would the volatility of the portfolio rise or fall? The expected return would remain constant, assuming only the correlation changes, 0. The volatility of the portfolio would increase due to the correlation term in the equation for the volatility of a portfolio.
Plot the expected return as a function of the portfolio volatility. A hedge fund has created a portfolio using just two stocks. The expected returns and standard deviations of the two stocks are given in the table below: Consider the portfolio in Problem Would the portfolio be more or less risky with this change?
An increase in the correlation would increase the variance of the portfolio; meanwhile, the expected return of the portfolio would remain constant. The riskiness of the portfolio would increase.
Beta Definition | Stock Market Definitions | Market News Video
If this transaction reduces the risk of his portfolio, what is the minimum possible correlation between the stock he shorted and his original portfolio? We gain the risk of the portfolio and lose the risk A has in common with the portfolio. Is holding this stock alone attractive compared to holding the portfolio in a? Can you improve upon your portfolio in a by adding this new stock to your portfolio?
No, it has the same expected return with higher volatility. Yes, adding this stock and reducing weight on the others will reduce risk while leaving expected return unchanged. The stocks have a correlation of 0. What is the expected return and volatility of the portfolio? What is the expected return and volatility standard deviation of your investment?
What portfolio has a higher expected return than your portfolio but with the same volatility? What portfolio has a lower volatility than your portfolio but with the same expected return? You are a financial advisor, and must choose one of the funds below to recommend to each of your clients.
Whichever fund you recommend, your clients will then combine it with risk-free borrowing and lending depending on their desired level of risk. Sharpe ratios of A,B and C are. Assume all investors want to hold a portfolio that, for a given level of volatility, has the maximum possible expected return. Explain why, when a risk-free asset exists, all investors will choose to hold the same portfolio of risky stocks. Investors who want to maximize their expected return for a given level of volatility will pick portfolios that maximize their Sharpe ratio.
The set of portfolios that do this is a combination of a risk free asset—a single portfolio of risk assets—the tangential portfolio.
Your broker suggests that you add a venture capital fund to your current portfolio. Calculate the required return and use it to decide whether you should add the venture capital fund to your portfolio. You have noticed a market investment opportunity that, given your current portfolio, has an expected return that exceeds your required return.
What can you conclude about your current portfolio? Your current portfolio is not efficient. You are currently only invested in the Natasha Fund aside from risk-free securities.
Currently, the risk-free rate of interest is 3. Your broker suggests that you add Hannah Corporation to your portfolio. Is your broker right? When you tell your finance professor about your investment, he says that you made a mistake and should reduce your investment in Hannah. Is your finance professor right? Is this the correct amount of Hannah stock to hold? Initial Portfolio Portfolio PortfolioNatasha Fund 0. Calculate the Sharpe ratio of each of the three portfolios in Problem What portfolio weight in Hannah stock maximizes the Sharpe ratio?
What is the Sharpe ratio of the Tanglewood Fund? What is the Sharpe ratio of your new portfolio? What is the optimal fraction of your wealth to invest in the venture fund? Use Excel and round your answer to two decimal places. Weight in venture fund Expected Return Volatility Sharpe Ratio Part a 0 0.
When the CAPM correctly prices risk, the market portfolio is an efficient portfolio. All investors will want to maximize their Sharpe ratios by picking efficient portfolios.
A big pharmaceutical company, DRIg, has just announced a potential cure for cancer. A friend calls to tell you that he owns DRIg. You proudly reply that you do too. Since you have been friends for some time, you know that he holds the market, as do you, and so you both are invested in this stock.
Both of you care only about expected return and volatility. DRIg made up 0. How is your wealth invested? How is he invested? Under the CAPM assumptions, a. What alternative investment has the lowest possible volatility while having the same expected return as Microsoft?
What is the volatility of this investment? What investment has the highest possible expected return while having the same volatility as Microsoft? What is the expected return of this investment? Under the CAPM assumptions, the market is efficient; that is, a leveraged position in the market has the highest expected return of any portfolio for a given volatility and the lowest volatility for a given expected return.
Suppose you group all the stocks in the world into two mutually exclusive portfolios each stock is in only one portfolio: Suppose the two portfolios have equal size in terms of total value , a correlation of 0. What is the expected return and volatility of the market portfolio which is a 50—50 combination of the two portfolios?
Does the CAPM hold in this economy? Is the market portfolio efficient? Value stocks have a higher sharpe ratio than the market, so mkt is not efficient. Johnson and Johnson Corporation Ticker: Under the CAPM assumptions, what is its expected return? Consider a portfolio consisting of the following three stocks: Compute the beta and expected return of each stock. Using your answer from part a, calculate the expected return of the portfolio.
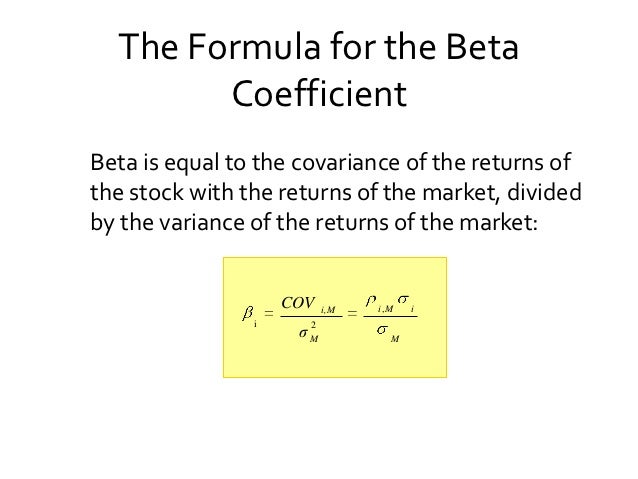
What is the beta of the portfolio? Using your answer from part c, calculate the expected return of the portfolio and verify that it matches your answer to part b. Suppose Intel stock has a beta of 2. What is the risk premium of a zero-beta stock? Does this mean you can lower the volatility of a portfolio without changing the expected return by substituting out any zero-beta stock in a portfolio and replacing it with the risk-free asset?
It is uncorrelated with the market, so there is no incremental risk from adding it to your portfolio. Note also that since the stock is positively correlated with itself which is part of the market , to have zero beta it must be negatively correlated with the other stocks.
Thus, it offsets risk that other stocks have. Thus, taking it out will not reduce risk. Chapter 12Estimating the Cost of Capital No, volatility includes diversifiable risk, and so it cannot be used to assess the equity cost of capital. Microsoft stock would need to have a beta of 1. Aluminum maker Alcoa has a beta of about 2. Suppose all possible investment opportunities in the world are limited to the five stocks listed in the table below.
What does the market portfolio consist of what are the portfolio weights? How much have you invested in Stock A? How many shares of Stock B do you hold? No trades are needed; it is a passive portfolio. If you hold the market portfolio, and as part of it hold shares of Best Buy, how many shares of Walt Disney do you hold? To maintain a portfolio that tracks this index, what trades would need to be made in response to daily price changes?
Is this index suitable as a market proxy? Sell winners, buy losers, to maintain an equal investment in each. The market portfolio should represent the aggregate portfolio of all investors. However, in aggregate, investors must hold more of larger market cap stocks; the aggregate portfolio is value weighted, not equally weighted. Could you use the same estimate for the market risk premium when applying the CAPM?
If not, how would you estimate the correct risk premium to use? No, expected return of this portfolio would be lower due to bonds. Compute the historical excess return of this new index. Does this mean the market risk premium we should use in the CAPM is negative?
Beta Definition - irudivupic.web.fc2.com
Investors were not expecting a negative return. To estimate an expected return, we need much more data. You need to estimate the equity cost of capital for XYZ Corp. You have the following data available regarding past returns: Use the CAPM to estimate an expected return for XYZ Corp. How does your answer to part c affect your estimate? Use d — CAPM is more reliable than average past returns, which would imply a negative cost of capital in this case! Ignore c , as alpha is not persistent.
Go to Chapter Resources on MyFinanceLab and use the data in the spreadsheet provided to estimate the beta of Nike and Dell stock based on their monthly returns from — You can use the slope function in Excel. You can use the intercept function in Excel.
Intercept Coefficients Standard t Stat P-value Lower UpperVW In mid, Ralston Purina had AA-rated, 6-year bonds outstanding with a yield to maturity of 3.
What is the highest expected return these bonds could have? Could these bonds actually have an expected return equal to your answer in part a? In mid, Rite Aid had CCC-rated, 6-year bonds outstanding with a yield to maturity of It believes the bonds will have a BBB rating.
What spread over AAA bonds will it have to pay? In fact, one might expect risk premia and betas to increase in recessions. Use CAPM to estimate expected return, using AAA rate as rf rate: Your firm is planning to invest in an automated packaging plant. Harburtin Industries is an allequity firm that specializes in this business. Consider the setting of Problem You decided to look for other comparables to reduce estimation error in your cost of capital estimate.
You find a second firm, Thurbinar Design, which is also engaged in a similar line of business. Explain the difference between your estimate in part a and part b. You decide to average your results in part a and part b , and then average this result with your estimate from Problem IDX Tech is looking to expand its investment in advanced security systems.
The project will be financed with equity. You are trying to assess the value of the investment, and must estimate its cost of capital. You find the following data for a publicly traded firm in the same line of business: What assumptions do you need to make? Assume comparable assets have same risk as project. Consider the following airline industry data from mid Use the estimates in Table Estimate the asset beta for each firm.
What is the average asset beta for the industry, based on these firms? Weston Enterprises is an all-equity firm with three divisions. The soft drink division has an asset beta of 0. The industrial chemicals division has an asset beta of 1. Estimate the value of each division. Individual divisions are either less risky or more risky. The founder of HHI, Harry Harrison, made his fortune in the fast food business.
He sold off part of his fast food empire, and purchased a professional hockey team. After a little research, you find that the average asset beta of other fast food restaurant chains is 0.
Your company operates a steel plant. Suppose the plant has an asset beta of 1. Estimate the value of the plant today assuming no growth. What is the value of the plant if you take this contract? Thus a higher cost of capital is appropriate.

You would like to estimate the weighted average cost of capital for a new airline business. Chapter 13Investor Behavior and Capital MarketEfficiency Assume that all investors have the same information and care only about expected return and volatility.
If new information arrives about one stock, can this information affect the price and return of other stocks? If so, explain why? When the new information arrives, it will change the attractiveness of this stock. If other stock prices do not change, then investors would want to increase their weight in this stock, implying they would not be holding the market portfolio. Assume that the CAPM is a good description of stock price returns. New news arrives that does not change any of these numbers but it does change the expected return of the following stocks: At current market prices, which stocks represent buying opportunities?
On which stocks should you put a sell order in? According to the CAPM, we should hold the market portfolio. But once new news arrives and we update our expectations, we may find profitable trading opportunities if we can trade before prices fully adjust to the news.
Assuming we initially hold the market portfolio, we can improve gain by investing more in stocks with positive alphas and less in stocks with negative alphas. Green Leaf, HanBel b. Rebecca Automobile and possibly NatSam although its alpha is close enough to zero that we might regard it as insignificant.
Suppose the CAPM equilibrium holds perfectly. Then the risk-free interest rate increases, and nothing else changes. Is the market portfolio still efficient? If your answer to a is yes, explain why. If not, describe which stocks would be buying opportunities and which stocks would be selling opportunities. Stocks with betas calculated using the market portfolio prior to the interest rate change greater than one will have positive alphas and so would be buying opportunities.
Similarly stocks with betas less than one will be selling opportunities. You know that there are informed traders in the stock market, but you are uninformed. Describe an investment strategy that guarantees that you will not lose money to the informed traders and explain why it works.
Invest in the market portfolio. Because the average investor must hold the market, by investing in the market you guarantee the average investor return. If the informed traders make higher returns than the average investor, somebody must make lower returns, so by holding the market you can guarantee that it is not you.
What are the only conditions under which the market portfolio might not be an efficient portfolio? The market portfolio can be inefficient so it is possible to beat the market only if a significant number of investors either 1. Do not have rational expectations so that they misinterpret information and believe they are earning a positive alpha when they are actually earning a negative alpha, or 2. Care about aspects of their portfolios other than expected return and volatility, and so are willing to hold inefficient portfolios of securities.
Explain what the following sentence means: The market portfolio is a fence that protects the sheep from the wolves, but nothing can protect the sheep from themselves. By investing in the market portfolio investors can protect themselves from being exploited by investors with better information than they have themselves. By choosing not to invest in the market portfolio, investors expose themselves to being exploited. If they do this because of overconfidence, they will lose money.
You are trading in a market in which you know there are a few highly skilled traders who are better informed than you are.
There are no transaction costs. Each day you randomly choose five stocks to buy and five stocks to sell by, perhaps, throwing darts at a dartboard. Over the long run will your strategy outperform, underperform, or have the same return as a buy and hold strategy of investing in the market portfolio?
Would your answer to part a change if all traders in the market were equally well informed and were equally skilled? You will underperform for two reasons: Of course in this problem only 2 will cause underperformance b.
This time the only source of losses are transaction costs. Why does the CAPM imply that investors should trade very rarely?
Because they should hold the market portfolio which is a value weighted portfolio and thus requires no retrading when prices change to maintain the value weights.
Your brother Joe is a surgeon who suffers badly from the overconfidence bias. In fact, he is uninformed like most investors. The uncertainty will be resolved in the next few hours. They also have submitted orders. Nobody else is trading in the stock. Describe what will happen to the market price once these orders are submitted if in fact the takeover will occur in a few hours.
What range of possible prices could result once these orders are submitted if the takeover will not occur. Trade will occur at some price in between and your brother will make negative profits.
To put the turnover of Figure The disposition effect causes investors to sell stocks that have appreciated and hold onto stocks that have depreciated. Thus investors are paying capital gains taxes that they could defer and deferring tax deductions they could take immediately. Because of the time value of money, these investors are therefore increasing their required tax obligations.
Consider the price paths of the following two stocks over six time periods: Assume you are an investor with the disposition effect and you bought at time 1 and right now it is time 3.
Assume throughout this question that you do no trading other than what is specified in these stocks. Which stock s would you be inclined to sell? Which would you be inclined to hold onto? How would your answer change if right now is time 6? What if you bought at time 3 instead of 1 and today is time 6?
What if you bought at time 3 instead of 1 and today is time 5? Suppose that all investors have the disposition effect.
The stock will pay no dividends. What equilibrium price will the stock trade for after the news comes out, that is, the price that equates supply and demand? Assume that you are the only investor who does not suffer from the disposition effect and your trades are small enough to not affect prices.
Without knowing what will actually transpire, what trading strategy would you instruct your broker to follow? Davita Spencer is a manager at Half Dome Asset Management.
After that her skills are spread too thin, so cannot add value and her alpha is zero. Assume that there are always investors looking for positive alpha and no investor would invest in a fund with a negative alpha. In equilibrium, that is, when no investor either takes out money or wishes to invest new money, a. How much money will Davita have under management? How much money will Half Dome generate in fee income?
Assume the economy consisted of three types of people. The portfolio consisting of all the informed traders has a beta of 1. What alpha do the informed traders make? What is the alpha of the passive investors? What is the expected return of the fad followers? What alpha do the fad followers make? Explain what the size effect is. The size effect is the empirical observation that firms with lower market capitalizations on average have higher average returns.
Assume all firms have the same expected dividends. If they have different expected returns, how will their market values and expected returns be related? What about the relation between their dividend yields and expected returns? Firms with higher expected returns will have lower market values, and firms with high dividend yields will have high expected returns.
Dell Inc.: NASDAQ:DELL quotes & news - Google Finance
Each of the six firms in the table below is expected to pay the listed dividend payment every year in perpetuity. Using the cost of capital in the table, calculate the market value of each firm.
Rank the three S firms by their market values and look at how their cost of capital is ordered. What would be the expected return for a self-financing portfolio that went long on the firm with the largest market value and shorted the firm with the lowest market value?
The expected return of a self-financing portfolio is the weighted average return of the constituent securities. Repeat using the B firms. Rank all six firms by their market values. How does this ranking order the cost of capital? Repeat part c but rank the firms by the dividend yield instead of the market value. What can you conclude about the dividend yield ranking compared to the market value ranking?
Consider the following stocks, all of which will pay a liquidating dividend in a year and nothing in the interim: Calculate the expected return of each stock. What is the sign of correlation between the expected return and market capitalization of the stocks?
What does the CAPM predict the expected return for each stock should be? Clearly, the CAPM predictions are not equal to the actual expected returns so the CAPM does not hold.
You decide to investigate this further. To see what kind of mistakes the CAPM is making, you decide to regress the actual expected return onto the expected return predicted by the CAPM. What is the intercept and slope coefficient of this regression?
What are the residuals of the regression in d? That is, for each stock compute the difference between the actual expected return and the best fitting line given by the intercept and slope coefficient in b.
What is the sign of the correlation between the residuals you calculated in e and market capitalization? What can you conclude from your answers to part b of the previous problem and part d of this problem about the relation between firm size market capitalization and returns?
The results do not depend on the particular numbers in this problem. You are welcome to verify this for yourself by redoing the problems with another value for the market risk premium, and by picking the stock betas and market capitalizations randomly.
Explain how to construct a positive-alpha trading strategy if stocks that have had relatively high returns in the past tend to have positive alphas and stocks that have had relatively low returns in the past tend to have negative alphas.
You buy stocks that have done well in the past and sell stocks that have done poorly. If you can use past returns to construct a trading strategy that makes money has a positive alpha , it is evidence that market portfolio is not efficient. If the market portfolio is efficient, then all stocks have zero alphas, and you could not construct any strategy that has a positive alpha.
Explain why you might expect stocks to have nonzero alphas if the market proxy portfolio is not highly correlated with the true market portfolio, even if the true market portfolio is efficient. Because the proxy portfolio is not highly correlated with the market portfolio, it will not capture some components of systematic risk.
The alphas reflect the risk components that the proxy portfolio is not capturing. Explain why if some investors are subject to systematic behavioral biases, while others pick efficient portfolios, the market portfolio will not be efficient.
Employees are already partially invested in their company due to their human capital. For Problems 26—28, refer to the following table of estimated factor betas.
Using the factor beta estimates in the table shown here and the expected return estimates in Table GE using the FFC factor specification. You are currently considering an investment in a project in the energy sector. The investment has the same riskiness as Exxon Mobil stock ticker: Using the data in Table MKT Factor XOM SMB 0.
You work for Microsoft Corporation ticker: MSFT , and you are considering whether to develop a new software product. The risk of the investment is the same as the risk of the company.
MKT Factor MSFT SMB 0. Chapter 14Capital Structure in a Perfect Market What is the NPV of this project? Suppose that to raise the funds for the initial investment, the project is sold to investors as an all-equity firm. The equity holders will receive the cash flows of the project in one year. How much money can be raised in this way—that is, what is the initial market value of the unlevered equity? What are the cash flows of the levered equity, and what is its initial value according to MM?
You are an entrepreneur starting a biotechnology firm. If your research is unsuccessful, it will be worth nothing. What is the total market value of the firm without leverage? Thus, in a perfect market the choice of capital structure does not affect the value to the entrepreneur. If Acort is unlevered, what is the current market value of its equity? Wolfrum Technology WT has no debt. Both events are equally likely.
What is the expected return of WT stock without leverage? What is the expected return of MM stock after the dividend is paid in part b? Suppose there are no taxes. After paying any interest on debt, both companies use all remaining free cash flows to pay dividends each year. Fill in the table below showing the payments debt and equity holders of each firm will receive given each of the two possible levels of free cash flows.
What is another portfolio you could hold that would provide the same cash flows? Suppose Alpha Industries and Omega Technology have identical assets that generate identical cash flows.
According to MM Proposition I, what is the stock price for Omega Technology? What arbitrage opportunity is available? What assumptions are necessary to exploit this opportunity? Sell 20 Omega, buy 10 alpha, and borrow Assumes we can trade shares at current prices and that we can borrow at the same terms as Omega or own Omega debt and can sell at same price. The firm has decided to use this cash to repurchase shares from investors, and it has already announced these plans to investors.
Currently, Cisoft is an all-equity firm with 5 billion shares outstanding. Cisoft has issued no other securities except for stock options given to its employees. What is the value per share? Management have decided to delever the firm by issuing new equity to repay all outstanding debt.
How many new shares must the firm issue? Suppose you are a shareholder holding shares, and you disagree with this decision.
Assuming a perfect capital market, describe what you can do to undo the effect of this decision. The transaction is scheduled to occur today. Assume perfect capital markets. What is the market value balance sheet for Zetatron i. After the new securities are issued but before the share repurchase? After the share repurchase? At the conclusion of this transaction, how many shares outstanding will Zetatron have, and what will the value of those shares be?
Explain what is wrong with the following argument: Therefore, risk-free debt allows the firm to get the benefit of a low cost of capital of debt without raising its cost of capital of equity. In fact, risk-free leverage raises it the most because it does not share any of the risk. Consider the entrepreneur described in Section According to MM Proposition I, what is the value of the equity?
What are its cash flows if the economy is strong? What are its cash flows if the economy is weak? What is the return of the equity in each case? What is its expected return? What is the risk premium of equity in each case? What is the sensitivity of the levered equity return to systematic risk? How does its sensitivity compare to that of unlevered equity? How does its risk premium compare to that of unlevered equity?
What is the debt-equity ratio of the firm in this case?

It is considering a leveraged recapitalization in which it would borrow and repurchase existing shares. Suppose Hardmon borrows to the point that its debt-equity ratio is 0. What will the expected return of equity be after this transaction?
Suppose instead Hardmon borrows to the point that its debt-equity ratio is 1. What will the expected return of equity be in this case? A senior manager argues that it is in the best interest of the shareholders to choose the capital structure that leads to the highest expected return for the stock. How would you respond to this argument? Returns are higher because risk is higher—the return fairly compensates for the risk. There is no free lunch. Suppose Microsoft has no debt and an equity cost of capital of 9.
What is the expected return of the stock after this transaction? If the risk of the debt does not change, what is the expected return of the stock after this transaction? If the risk of the debt increases, would the expected return of the stock be higher or lower than in part i?
The debt will share some of the risk. Hubbard does a leveraged recapitalization, issuing debt and repurchasing stock, until its debt-equity ratio is 0. The value of the risk-free debt is unchanged.
Indell currently has risk-free debt as well. With perfect capital markets, what will be the beta of Indell stock after this transaction? If the debt is risk-free: The only change in the equation is the value of equity.
Yerba Industries is an all-equity firm whose stock has a beta of 1. What is the beta of Yerba stock after this transaction? What is the expected return of Yerba stock after this transaction?
Does this change benefit shareholders? The stock price does not change. It falls due to higher risk. You are CEO of a high-growth technology firm. How can you explain the difference? Suppose Zelnor decides to grant a total of 10 million new shares to employees as part of a new compensation plan. The firm argues that this new compensation plan will motivate employees and is a better strategy than giving salary bonuses because it will not cost the firm anything.
Why is issuing equity costly in this case? Issuing equity at below market price is costly. Chapter 15Debt and Taxes If Pelamed had no interest expenses, what would its net income be? How does it compare to your answer in part b? For the same increase in interest expense, how will free cash flow change?
Free cash flow is not affected by interest expenses. Suppose the firm has no debt and pays out its net income as a dividend each year. What is the value of equity?
What is the value of debt? What is the difference between the total value of the firm with leverage and without leverage? The difference in part c is equal to what percentage of the value of the debt? Year 0 Debt 35 Interest 28 21 14 7 0 Tax Shield 2. What is the present value of the interest tax shields from this debt? Year 0 1 23 45 Debt 75 50 25 00 Interest 10 7. The firm will pay interest only on this debt.
What is its annual interest tax shield? What is the present value of the interest tax shield, assuming its risk is the same as the loan?
What is the present value of the interest tax shield in this case? What is the present value of the interest tax shield today? In addition to 6. As the outstanding balance declines, so will the interest tax shield. This is the present value of the future taxes Safeco will pay on the interest earned on its reserves. Rogot Instruments makes fine Violins and Cellos. Summit Builders has a market debt-equity ratio of 0. Suppose NatNah decides to increase its leverage and maintain a market debt-to-value ratio of 0.
Restex maintains a debt-equity ratio of 0. Acme plans to maintain this same debt-equity ratio in the future. The firm pays an interest rate of 7. What is the value of Milton Industries without leverage? What is the value of Milton Industries with leverage? Suppose Microsoft has 8.
Kurz will pay interest only on this debt, and it has no further plans to increase or decrease the amount of debt. How many shares will Kurz repurchase? Would shareholders sell for this price? What is the lowest price Rally can offer and have shareholders tender their shares? What will its stock price be after the share repurchase in that case? Just before the share repurchase: Therefore, shares will be willing to sell at this price. It will pay this interest expense by cutting its dividend.
How much will debt holders receive after paying taxes on the interest they earn? By how much will the firm need to cut its dividend each year to pay this interest expense? Business Fashion Health Entertainment Music Sports Art Auto. The words you are searching are inside this book. To get more targeted content, please make full-text search by clicking here. Home Explore Corporate Finance Solutions Manual.
You can publish your book online for free in a few minutes! Discover the best professional documents and content resources in FlipHTML5 Document Base. Corporate Finance Solutions Manual Published by getexcool. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 12Estimating the Cost of Capital Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 13Investor Behavior and Capital MarketEfficiency Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 14Capital Structure in a Perfect Market Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 15Debt and Taxes