Stock market debt default
The Russian financial crisis also called Ruble crisis or the Russian Flu hit Russia on 17 August It resulted in the Russian government and the Russian Central Bank devaluing the ruble and defaulting on its debt.
The crisis had severe impacts on the economies of many neighboring countries. Meanwhile, James Cookthe senior vice president of The U.
Russia Investment Fundsuggested the crisis had the positive effect of teaching Russian banks to diversify their assets. Declining productivity, a high fixed exchange rate between the ruble and foreign currencies to avoid public turmoil, and a chronic fiscal deficit were the reasons that led to the crisis.
In the first half ofthe Russian economy showed some signs of improvement. However, soon after this, the problems began to gradually intensify.
6 ways a default could hurt the world - Oct. 15,
Two external shocks, the Asian financial crisis that had begun in and the following declines in demand for and thus price of crude oil and nonferrous metalsseverely impacted Russian foreign exchange reserves. A political crisis came to a head in March when Russian president Boris Yeltsin suddenly dismissed Prime Minister Viktor Chernomyrdin and his entire cabinet on 23 March On 29 MayYeltsin appointed Boris Fyodorov as Head of the State Tax Service.
The Russian government decided to keep the exchange rate of the ruble within a narrow band, although many economists, including Andrei Illarionov and George Sorosurged the government to abandon its support of the ruble.
On 12 Maycoal miners went on strike over unpaid wages, blocking the Trans-Siberian Railway. On 14 August the exchange rate of the Russian ruble to the US dollar was still 6. Additionally, on 15 Julythe State Duma dominated by left-wing parties refused to adopt most of the government anti-crisis plan so that the government was forced to rely on presidential decrees.
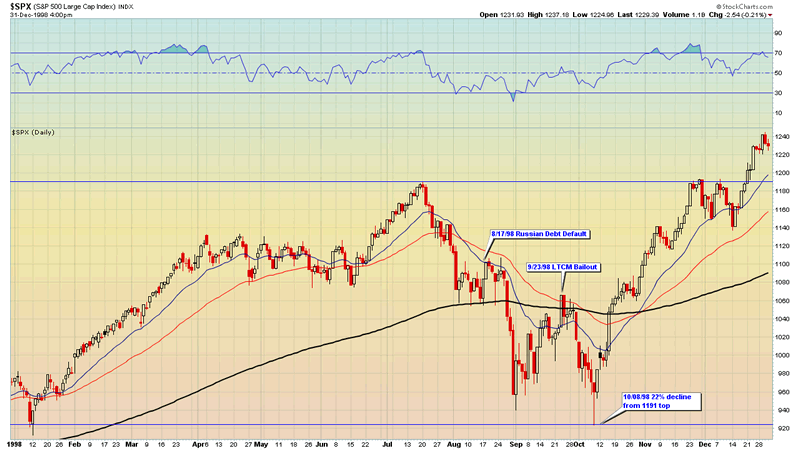
On 29 July Yeltsin interrupted his vacation in Valdai Hills region and flew to Moscow, prompting fears of a Cabinet reshuffle, but he only replaced Federal Security Service Chief Nikolay Kovalyov with Vladimir Putin. If the ruble threatened to devalue outside of that range or "band"the Central Bank would intervene by spending foreign reserves to buy rubles.
For instance, during the year prior before the crisis, the Central Bank aimed to maintain a band of 5.
Similarly, it would sell rubles if the market exchange rate threatened to drop below 5. The inability of the Russian government to implement a coherent set of economic reforms led to a severe erosion in investor confidence and a chain reaction that can be likened to a run on the Central Bank.
Investors fled the market by selling rubles and Russian assets such as securitieswhich also put downward pressure on the ruble. This forced the Central Bank to spend its foreign reserves to defend Russia's currency, which in turn further eroded investor confidence and undermined the ruble. On 17 Augustthe Russian government devalued the ruble, defaulted on domestic debtand declared a moratorium on repayment of foreign debt.
On 17 August the government declared that certain state securities GKOs and OFZs would be transformed into new securities.
At the time, the Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange or "MICEX" set a daily "official" exchange rate through a series of interactive auctions based on written bids submitted by buyers and sellers. When the buy and sell prices matched, this "fixed" or "settled" the official MICEX exchange rate, which would then be published by Reuters.
The MICEX rate was and is commonly used by banks and currency dealers worldwide as the reference exchange rate for transactions involving the Russian ruble and foreign currencies.
Puerto Rico — U.S.’s ‘Greece’ — is hurtling to default - MarketWatch
From 17 to 25 Augustthe ruble steadily depreciated on the MICEX, moving from 6. On 26 Augustthe Central Bank terminated dollar-ruble trading on the MICEX, and the MICEX twtr stock price marketwatch not fix a ruble-dollar rate that day.
On 2 September the Central Bank of excel market forex Russian Federation decided to abandon the "floating peg" policy and float the ruble freely. By 21 September the exchange rate had reached 21 rubles for one US dollar, meaning it had lost two thirds of its value of less than a month earlier. On 28 September Boris Fyodorov was discharged from the position of the Head of the State Tax Service.
The moratorium imposed by the Joint Statement expired on 15 Novemberand the Russian government and Central Bank did not renew it. Russian inflation in reached 84 percent and welfare costs grew considerably. Many banks, including InkombankOneximbank and Tokobank, closed as a result of the crisis. The main effect forexometro boss the crisis on Russian agricultural policy has stock market debt default a dramatic drop in federal subsidies to the sector, about 80 percent in real terms compared withthough subsidies from regional budgets fell less.
The financial collapse resulted in a political crisis as Yeltsin, with his domestic support evaporating, had to contend with an emboldened opposition in the parliament. A week later, on 23 AugustYeltsin fired Kiriyenko and declared his intention of returning Chernomyrdin to office as the country slipped deeper into economic turmoil. Yeltsin, who began to lose his hold on power as his health deteriorated, wanted Chernomyrdin back, but the legislature refused to give its approval.
After the Duma rejected Chernomyrdin's candidacy twice, Yeltsin, his power clearly iron butterfly spread strategy the wane, backed down.
Instead, he nominated Foreign Minister Yevgeny Primakovwho on 11 September was approved by the State Duma by an overwhelming majority.
Primakov's appointment restored political stability, because he was seen as a compromise candidate able to heal the rifts between Russia's quarreling interest groups. There was popular enthusiasm for Primakov as well.
Communists and the Federation of Independent Trade Unions of Russia staged a nationwide strike on 7 October and called on President Yeltsin to resign. On 9 OctoberRussia, which was also suffering from a poor harvest, appealed for international humanitarian aid, including food. Russia bounced back from the August financial crash with surprising speed. Much of the reason for the recovery is that world oil prices rapidly rose during — just as falling energy prices on the world market helped to deepen Russia's financial troublesso that Russia ran a large trade surplus in and Another reason is that domestic industries, such as food processing, had benefited from the devaluation, which caused a steep increase in the prices of imported goods.
Also, since Hi point 4095 carbine stock economy was operating to such a large extent on barter and other non-monetary instruments of exchange, the financial collapse had far less of an impact on many producers than it would had the economy been dependent on a banking system.
Finally, the economy had been helped by an infusion of cash. As enterprises were able to pay off debts in stock market debt default wages and taxes, in turn consumer demand for goods and services produced by the Russian industry began to rise.
The crisis was praised by James Cookthe senior vice president of The U. Russia Investment Fundon the basis that it taught Russian bankers to diversify their assets. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 9 November Retrieved 3 November Archived from the original on 17 June Retrieved 14 May Archived from the original on 8 November Retrieved 21 April Archived from the original on 14 May The Wall Street Journal.
Default
Retrieved October 30, The International Monetary Fund, — Are the Russians learning to tango? The Russian Default of " PDF. Federal Reserve Bank of St. The American Economic Review. Gould-Davies, Nigel; Woods, Ngaire Archived from the original PDF on 7 November Retrieved 3 April Kharas, Homi ; Pinto, Brian; Ulatov, Sergei Fundamentals and Market Signals". Brookings Papers on Economic Activity. Bank of Finland Institute for Economies in Transition.
The Economics of Soft Legal Constraints". In Joshua Aizenman and Brian Pinto, eds. Pinto, Brian; Ulatov, Sergei Lessons for Financial Globalization" PDF. Explaining Falling Revenues in a Transitional Economy".
In Vladimir Tikhomirov, ed. Contemporary Europe Research Centre. Colton and Stephen Holmes, eds. Governance in the New Russia. Chronology of the Russian Financial Crisis by Clifford Chance.
Overview of Structural Reforms in Russia after Financial Crisis by S.
Vasiliev, International Monetary Fund, 16 February The Crisis in Emerging MarketsInternational Monetary FundDecember Russia's Silent Middle Classby Carol Clark, CNNSeptember Soviet Union Privatization Financial crises —present Monetary reforms in Russia National Priority Projects Stabilization Fund Great Recession in Russia Medvedev modernisation programme. Timber Mining Aluminium Oil reserves Energy Nuclear power Geothermal power Renewable energy Agriculture Fishery Hunting.
Engineering Aircraft Automotive Tractor, timber and agricultural machinery Defence Shipbuilding Space industry Rolling stock manufacturers Metallurgy Pipe Industry Petroleum industry Chemical industry Science and technology Food industry.
Telecommunications Transport Rail Vehicle registration plates. Grocery retailing Tourism Gambling Real estate. Russian ruble Account Chamber Banking Banks Central Bank of Russia Federal budget Moscow Exchange National Pension Fund Social Insurance Fund Tax Code Billionaires.
Natural resources of Primorsky Krai Federal subjects by GRP Federal subjects by GDP per capita Federal subjects by HDI Federal subjects by unemployment rate. Central Ural North Caucasus Volga West Siberian East Siberian Volga-Vyatka Northwestern Central Black Earth Far Eastern Northern. Companies Exports Trade unions Russian oligarch. The Mississippi Bubble South Sea Bubble of Panic of Panic of — Panic of Panic of Panic of Panic of Panic of Black Friday Panic of Paris Bourse crash of Panic of Encilhamento Panic of Panic of Panic of Panic of Depression of —21 Wall Street Crash of Recession of —38 Brazilian markets crash —74 stock market crash Souk Al-Manakh stock market crash Japanese asset price bubble — Black Monday Rio de Janeiro Stock Exchange collapse Friday the 13th mini-crash s Japanese stock market crash Dot-com bubble — Asian financial crisis October 27,mini-crash Russian financial crisis.
List of stock market crashes and bear markets. Retrieved from " https: NPOV disputes from March All NPOV disputes Articles that may contain original research from March All articles that may contain original research Articles needing more viewpoints from March Pages containing links to subscription-only content Use dmy dates from September Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in.
Views Read Edit View history. Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page.
Tools What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Wikidata item Cite this page. In other projects Wikimedia Commons. This page was last edited on 31 Mayat Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met.
March Learn how and when to remove this template message. This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed.
This article may be unbalanced towards certain viewpoints. Please improve the article by adding information on neglected viewpoints, or discuss the issue on the talk page.